What it takes to be a CORONA survivor?
This article covers every aspect to this statement “What will happen if I get Corona? Either I die or survive! ..... No big deal”. But here I say YES it’s a big deal. After reading this article you may say it’s better to die than to live as a corona survivor. Don’t worry I will provide you ways how to keep corona away from you in upcoming article. So, Let’s discuss why is it a big deal to be a CORONA survivor!
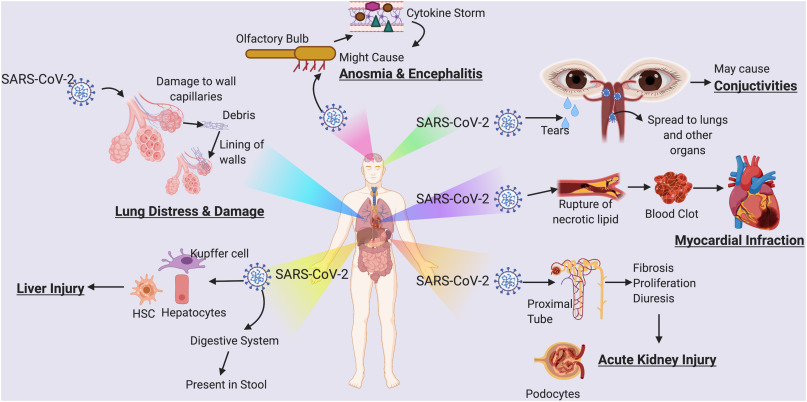
At first let’s discuss about the possible organ damage associated with COVID-19 and the long-term issues that may stem from them. As we all know now that the SARS-CoV-2 mainly affects the older, immune deficient and people who have had any previous medical conditions related to lungs, kidney, heart and the GI tract (Meredith et al., 2020). In this article we are trying to cover different case study which suggest we might need post-acute care to recuperate from any further infections or multi-organ damage for COVID-19 recovered patients. Many cases of psychological stress and multi-organ failure are coming up in recovered patients. Apart from damaging Gastrointestinal (GI) tract and lungs recent studies have shown it affects your HEART, KIDNEY and even worse affecting your BRAIN leading to emergence of new neurodegenerative disease.
We all know easy route for corona to enter our body is through nose or mouth. Eyes can also exist as a transmission route for viral spreading. The patients might also have ocular related symptoms including conjunctivitis, chemosis, swelling of the conjunctiva, epiphora or overflow of tears onto the face. The virus initially enervates the conjunctiva of eye, the tears act as the route of transmission which then spread infection to other organs in the human system (Sommer, 2020).
COVID-19 affecting our Lungs and Heart
The prime most symptom of SARS-CoV-2 infection is pneumonia. Activation of alveolar macrophages results in lung fibrosis and damage. Among the 46,959 patients (collective study from 31 articles), 28.8% of the individuals exhibited ARDS(Acute respiratory distress syndrome), when the chest Computed tomography(CT) was considered, 75.5% of them had double pneumonia, while 20.4% exhibited unilateral pneumonia(Cao et al. (2020)). The symptoms are so inter-related to each other that consequence of one symptom leads to other organ attack.
Pneumonia could cause inflammation throughout the body forming plaque in the arteries which can lead to heart attacks. Many reports from various countries such as China, Italy and the USA have confirmed that SARS-CoV-2 can affect the heart muscle causing cardiac failure or myocarditis (Markian, 2020). In the heart, this viral infection can rupture the necrotic lipid core forming blood clots resulting in myocardial infarction.
COVID-19 affects our Nervous system
In the brain, the olfactory bulb gets infected by SARS-CoV-2, which leads to the inability of smell and might also trigger neurodegenerative diseases in the COVID-19 recovered patients. In a recent case report from the USA, a 50-year old COVID-19 woman patient was manifested with acute necrotizing encephalopathy (blood-brain barrier vessel leakage in the thalamus) (Poyiadji et al., 2020). Another report of a 74-year-old COVID-19 patient having Parkinson's disease and chronic lung disease also displayed neurological symptoms such as inability to speak and seizures (Filatov et al., 2020).
Multi-organ failure (Liver and Kidney failure)
In a 55-day old infant infected with SARS-CoV-2, liver damage was observed due to an increase in level of liver enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT)) (Cui et al., 2020).
Acute kidney injury (AKI) has been reported in SARS-CoV-2 patients due to activation of inflammasome and apoptosis pathways (Yang et al., 2020). These activated Nucleotide-binding domains (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) signaling can cause pyroptosis and cell death resulting in inflammation and kidney injury (Li et al., 2019).
It affects our Gastro-Intestinal tract too!
Common COVID-19 related GI symptoms include nausea, anorexia, vomiting, abdominal pain and gastrointestinal bleeding. At the initial stage of COVID-19, patients have increased rates of sore throat, dizziness, fever, headache, fatigue and shortness of breath, showing that GI symptoms may occur. This is conclusive with a study in which a neonate first exhibited GI symptoms, including vomiting and milk refusal (Zhu et al., 2020) before other symptoms of COVID-19 manifested.
COVID-19 in our POOP?
Implication of gastrointestinal conditions in COVID-19 leads to presence of viral particles in faecal matter (Tian et al., 2020). This supports the fact the virus found in our sewage samples because of open latrine that runs through our houses to the rivers. Screening of virus through fecal samples specially in sewage helps to tract epidemic effectively. Can we imagine the impact we have done to the environment? We consume same food that has been irrigated by those rivers. Time has come to think and rebuilt those systems.
Psychophysical symptoms
Depression, fear and anxiety may persist for a longer time for most of the COVID-19 recovered patients. Some of the recovered patients will still have some lingering effects of the virus as well as of the hospital environment. Such situations would make the recovered patients feel paranoid. For the infected, as well as few recovered patients, during the quarantine period being devoid from human contact might increase the chances of psychological symptoms. This would make the COVID-19 recovered patients prone to physical, cognitive as well as few psychological problems which could also be termed as post-intensive care syndrome. Unaffected people will also fear to meet people and try hard not to get infected by any means. The aftermath of the disease would be persistent in the back of everyone’s minds. Thus, it is extremely important to maintain mental balance while returning to normalcy.
A WAY FORWARD:
According to the WHO, people at the age group of 10–50 are likely to get recovered from the disease since the death rate for this age category is well below 1%. From Covid-19 lesson to be learned is to maintain hygiene, sanitation, do proper waste management, focus on physical and mental well-being and at last working on sustaining nature.
What things can work always to avoid such situation in future?
- Immediate medical action: Building temporary hospitals in different local areas. They don’t have to be well equipped but should have at least primary medicines and emergency service to handle severe cases.
- Rapid screening of disease: This helps to screen out infected people from non-infected ones. Solve problem of occupied bed and focus can be given to infected people only until full recovery.
- Investment on Research: Government should allocate immediate fund and make flexible policy for doing research. Rapid diagnostic detection kit can be made in less time in own country itself. Keeping track of patients helps to understand effects if infection accurately. Knowing general and biochemical characteristics of that disease help to prevent its future outbreak.
- Mandatory monitoring health status of recovered patients: The disease can have long term effect or can be capable of secondary infection. Observational investigation on a larger cohort would help us to understand the in-depth prognosis as well as the pathogenesis of the COVID-19 disease.
- Guidelines for work safety: Guidelines that is applicable to every workplace keeping health safety in priority should be made. This help to operate business/work in safe manner. Lockdown is never an option. It creates long economic crisis. Running awareness program to follow these guidelines makes everyone responsible and gradually everything starts to come in normal way. New rules and regulations should be made.
- Saving vulnerable groups: In pandemic situation government is only one life savior. Vulnerable groups can be any one. They can be post-pandemic patients who have lost capability to do work, staffs who have lost their jobs, business owners, etc. Everyone is affected. Government should be able to provide direction if not support. Making tax and interest free from bank loans helps to flow cash. Manpower can be exchanged. Eg. Engineers were helping farmers to harvest their crops in Europe. Government hired local people from different profession to distribute these foods door to door in safe way.
COVID-19 recovered patients may have psychological stress due to their infection and may be ambiguous about their acceptance in society post infection. Hence, it is essential to conduct the follow-up studies in COVID-19 recovered patients to determine if they have any other detrimental illnesses. These kinds of studies would help uncover if COVID-19 recovered patients needed post-acute care to recuperate from any further infections or multi-organ damage.
LASTLY…….
If these things are regulated not only COVID-19 we can fight against any pandemic.
I have to say we were lucky this time. Corona can be fought with immunity. We had that immunity and those immune boosting foods in our diet which is saving us. But we will not be lucky next time! If it was an air borne infection and if our immunity doesn’t have defense mechanism against it, we can imagine what will be. This is just a beginning; a lot of more deadly things are coming in near future. Nothing is small, if late even bigger movements cannot make things right. Begin from yourself for the new change, for the new normal.
References:
- Picture and main article Reference: Vellingiri Balachandar, Iyer Mahalaxmi, Mohandevi Subramaniam, Jayaramayya Kaavya, Nachimuthu Senthil Kumar, Gracy Laldinmawii, Arul Narayanasamy, Patur Janardhana Kumar Reddy, Palanisamy Sivaprakash, Sivaprakash Kanchana, Govindasamy Vivekanandhan, Ssang-Goo Cho,Follow-up studies in COVID-19 recovered patients - is it mandatory?,Science of The Total Environment,Volume 729,2020,139021,ISSN 0048-9697,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139021.
- Cao et al., 2020.Y. Cao, X. Liu, L. Xiong, K. Cai.Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J. Med. Virol. (2020), 10.1002/jmv.25822
- Filatov et al., 2020.A. Filatov, P. Sharma, F. Hindi, S.E. Patricio.Neurological complications of coronavirus disease (COVID-19): encephalopathy.Cureus, 12 (3) (2020), p. e7352, 10.7759/cureus.7352
- H. Zhu, L. Wang, C. Fang, S. Peng, L. Zhang, G. Chang, S. Xia, W. Zhou.Clinical analysis of 10 neonates born to mothers with 2019-nCoV pneumonia.Transl. Pediatr., 9 (1) (2020), pp. 51-60, 10.21037/tp.2020.02.06
- L. Li, W. Tang, F. Yi.Role of inflammasome in chronic kidney disease.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 1165 (2019), pp. 407-421, 10.1007/978-981-13-8871-2_19
- Markian, 2020.H. Markian.Heart Damage in COVID-19 Patients Puzzles Doctors Scientific American (2020). (Published on 6th April, 2020)
- Meredith et al., 2020.W. Meredith, C.F. Jennifer, K. Jocelyn, M. Catherine.How does coronavirus kill? Clinicians trace a ferocious rampage through the body, from brain to toes Science (2020), 10.1126/ science.abc3208.Published on 17th April, 2020
- Poyiadji et al., 2020.N. Poyiadji, G. Shahin, D. Noujaim, M. Stone, S. Patel, B. Griffith.COVID-19–associated acute hemorrhagic necrotizing encephalopathy: CT and MRI features Radiology (2020), 10.1148/radiol.2020201187
- Qing et al., 2020.H. Qing, Z. Li, Z. Yang, M. Shi, Z. Huang, J. Song, Z. Song.The possibility of COVID-19 transmission from eye to nose.Acta Ophthalmol., 2020 (2020), 10.1111/aos.14412
- Tian et al., 2020.Y. Tian, L. Rong, W. Nian, Y. He.Gastrointestinal features in COVID-19 and the possibility of faecal transmission.Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. (2020), 10.1111/apt.
- X. Yang, Y. Yu, J. Xu, H. Shu, J. Xia, H. Liu, Y. Wu, L. Zhang, Z. Yu, M. Fang, T. Yu, Y. Wang, S. Pan, X. Zou, S. Yuan, Y. Shang.Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study.Lancet Respir. Med. (2020), 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5
Article By:
- Ms. Sumeena Karki
Biotechnologist, Central Department of Biotechnology
Founder and CEO, RARA Biotech
